Online Italian courses that get you to speak
The only all-in-one solution that takes you from structured audio lessons and quick reads to personalized, real-world conversations with an AI tutor.
- No credit card needed
- Secret coupon inside

Rave Reviews by Learners









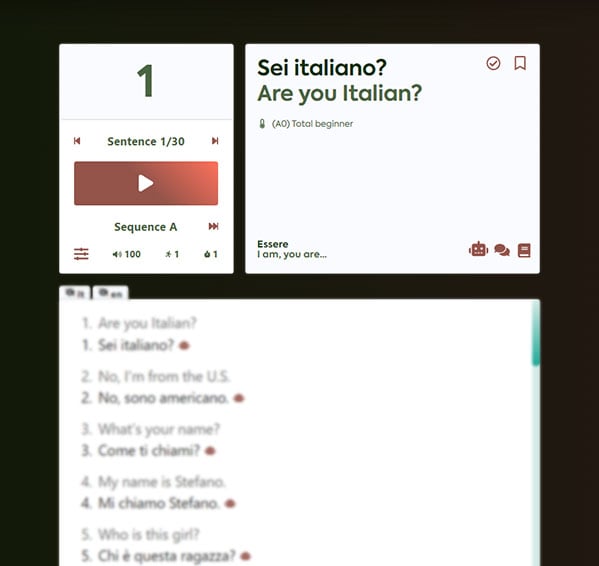
Audio lessons
Research proves that learning through speech and repetition is effective, mimicking the way we picked up our first language as kids.
My course plan introduces you to grammar patterns and helps you retain vocabulary.
You’ll not only improve your Italian but start thinking in the language in a matter of days.
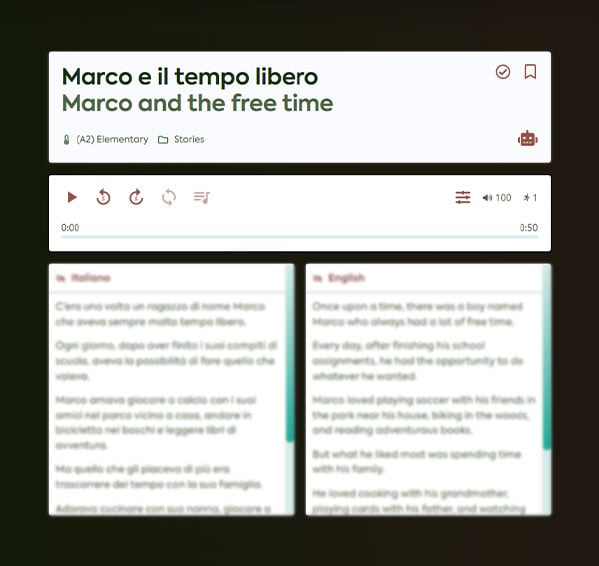
Bilingual readings
Engage with Italian through my diverse collection of stories, news articles, and real-life dialogues to put your learning into context and make it enjoyable.
Each piece comes with audio and dual-language transcripts, allowing you to immerse yourself in just one minute, enhancing language retention.
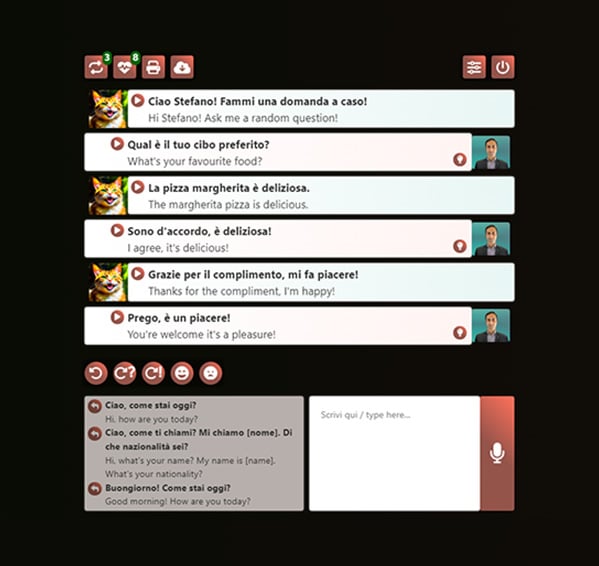
Conversations with AI tutor
Meet your personal AI tutor, designed for engaging, meaningful conversations in Italian. It gets to know you, creating realistic dialogue scenarios tailored just for you.
With real-time audio feedback and easy-to-follow bilingual transcripts, you’ll be amazed at how quickly you’re not just learning, but actually conversing in Italian.
Your Italian
Language Coach
As a serial language learner, I’ve lectured in polyglot clubs about my method. After learning 12 languages, I can tell you that we all master languages by listening and mimicking.
With my method, you’ll be speaking Italian from Lesson 1.
6 yrs
In Teaching

2000+
Live Classes Taught
Stefano Lodola
Italian language tutor, translator, polyglot

"Stefano is a fantastic educator. I recommend his lessons to all language lovers."

"Stefano knows how languages are learned. His course is the best of the learning resources I've tried."

Omniglot.com
Chinese-Italian Translator – Omniglot.com



